advanced
OTC trading is a method of trading financial assets, including cryptocurrencies, that takes place directly between two parties without the oversight of an exchange. This decentralized form of trading is particularly favored by large players, such as hedge funds, who are looking for a private and efficient way to execute large trades without affecting the market price. Naturally, the format also attracts many crypto investors.
However, OTC trading has its own set of challenges. Due to less regulatory oversight, it could suffer from a lack of investor interest, eroding its liquidity. In this article, I will outline both the benefits and the risks you may encounter when trading OTC stocks or crypto. Let’s dive in!
Over-the-Counter (OTC) trading definition
Over-the-Counter (OTC) trading refers to a method of trading that takes place directly between two parties without the supervision of an exchange. This trading is done through a decentralized market rather than on a centralized exchange. In OTC markets, trading can span a wide variety of assets – from commodities to financial instruments such as stocks and cryptos. The key point here is that OTC trading bypasses the traditional stock exchange media.

What is an OTC market?
An over-the-counter market is a decentralized market where the trading of financial instruments, such as stocks, commodities, currencies or derivatives, takes place. This is in contrast to auction markets (such as the New York Stock Exchange or Nasdaq), which are characterized by a physical location.
The OTC Markets Group, a critical player in this field, categorizes OTC-traded companies into three tiers based on various factors, including financial standards, corporate governance and disclosure practices. These levels are OTCQX (the top level), OTCQB (the venture market), and OTC Pink (the pink market).
While market participants can trade blue-chip stocks, most OTC securities come from smaller companies. These can be penny stocks of early stage or growth companies or securities of shell companies and larger foreign companies that do not meet the requirements to be listed on a major US stock exchange.
Can you trade crypto on OTC markets?
Yes, cryptocurrencies can indeed be traded on OTC markets. In fact, OTC trading desks have become a notable part of the cryptocurrency world, especially for larger transactions. Crypto OTC transactions can take place via email, private messages, or special electronic platform trading systems.
OTC trading allows you to bypass third parties and exchange crypto in a more direct way.
Like the way market makers facilitate the buying and selling of traditional OTC securities, they also play a vital role in the crypto OTC market, providing liquidity and determining the share price of the crypto coins. The market makers ensure that there is enough trading volume to allow market participants to buy or sell a significant amount of a specific cryptocurrency without substantially changing the market price.
Types of OTC Securities
OTC markets facilitate trading in a variety of securities, including:
- Stocks – often penny stocks or stocks of smaller companies, as well as stocks of larger foreign companies that are not eligible for listing on a major stock exchange.
- Derivatives – these are complex financial instruments whose value is derived from underlying assets such as stocks, bonds, commodities or cryptocurrencies.
- Bonds – corporate bonds, municipal bonds and government bonds can be traded OTC.
- Cryptocurrencies – given the relatively decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies, OTC markets are a popular place to trade these digital assets, especially for large-scale transactions.
- Bank Certificates – Bank Certificates of Deposit (CDs) can also be traded on OTC markets.
The pros and cons of OTC trading
Advantages:
- Flexibility and convenience. OTC markets operate 24/7, allowing market participants to trade at any time. This is beneficial for cryptos, which also trade 24 hours a day.
- Privacy. Since OTC transactions do not need to be immediately reported publicly, they offer traders more privacy.
- Less market impact. Large transactions in OTC markets are less likely to affect a security’s market price, making them ideal for large transactions.
Cons:
- Additional risk. OTC trading carries additional risks due to the lack of regulatory oversight. This risk can be especially pronounced with penny stocks and cryptocurrencies, which are often subject to price manipulation.
- Lack of transparency. OTC markets lack the transparency of exchanges, making it more difficult for traders to establish a fair market price.
- Regulatory Compliance. For foreign companies in particular, it can sometimes be complex and time-consuming to comply with regulations when trading OTC.
- Liquidity risk. Some OTC securities may be less liquid than securities traded on exchanges, which may make it more difficult for traders to buy or sell them without affecting the market price.
In conclusion, while OTC markets provide an alternative trading platform for a range of securities, including cryptocurrencies, they also come with their own unique risks and challenges. Therefore, potential traders should carefully consider these factors and possibly seek professional advice before diving into OTC trading.
OTC vs Exchange
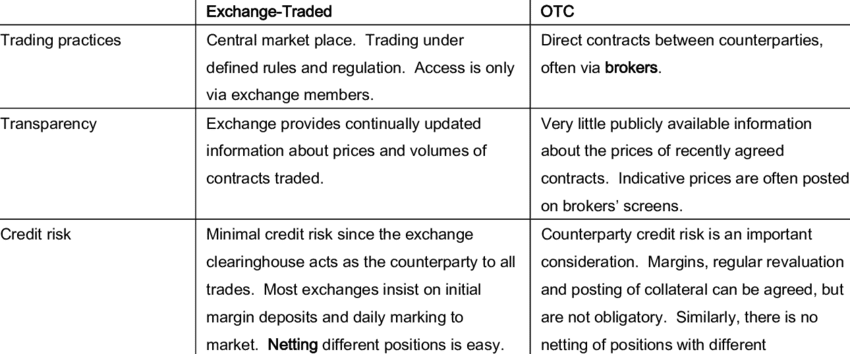
OTC and exchange trading differ fundamentally in the way trades are executed. In the OTC (Over-the-Counter) market, trading is done directly between two parties without the supervision of an exchange. It is essentially a decentralized market with no physical location.
On the other hand, stock market trading, which takes place on exchanges such as the NYSE and Nasdaq, is centralized. All transactions are executed and settled through the exchange platform, ensuring transparency and regulatory compliance. However, in OTC markets, a broker-dealer network is responsible for executing transactions.
Reporting standards also differ. OTC markets often have more lenient reporting requirements compared to exchanges. For example, while some OTC securities report to the SEC (the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission), many others do not. This flexibility can be beneficial to smaller companies that cannot meet the strict capital requirements of major exchanges.
How to buy OTC stocks and crypto
Buying OTC stocks and cryptocurrencies isn’t really any different from buying other types of securities. You need to follow these general steps:
- Find a broker: Choose a broker who has access to the OTC market. Make sure it is registered with the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA). If you’re looking for OTC crypto, choose a platform that has good reviews and proven reliability – and don’t forget to check out their security measures.
- Do your research: Research the investment benefits of the OTC stocks or crypto you want to buy. For stocks, this may mean reviewing the pink sheet listings.
- Place an order: Once you have decided on an investment, place your order on your chosen platform. Be sure to specify the ticker symbol of the stock or cryptocurrency.
Remember that OTC transactions are less regulated than transactions on major exchanges. So it is essential to exercise due diligence before making investment decisions.
FAQ
What are OTC derivatives?
OTC derivatives are contracts that are traded (and negotiated over the counter) directly between two parties without going through an exchange or other intermediary. These derivative transactions may involve various financial instruments such as currencies, interest rates, commodities or indices.
Unlike standardized exchange traded derivatives, OTC derivatives are customized according to counterparty needs. The terms of these derivatives may be modified to meet future payments, notional amounts and other specific needs of the parties involved.
OTC derivatives gained prominence during the 2008 financial crisis as they were a major contributor to the instability of the financial system. As a result, the European Union and other jurisdictions have implemented regulations to increase transparency and mitigate risk associated with OTC derivative transactions.
What does OTC mean?
OTC stands for over the counter. In financial markets, OTC refers to the process of how securities are traded for companies that are not listed on an exchange. Securities traded over-the-counter are traded through a broker-dealer network rather than on a centralized exchange. These securities can be stocks, bonds, derivatives or cryptocurrencies.
Are OTC Stocks Safe?
It’s important to remember that while OTC stocks can offer great profit opportunities, they also come with risk. So it is critical for investors to thoroughly research all OTC stocks before investing and to seek advice from a financial advisor or broker who is familiar with the OTC market.
Since the safety of OTC stocks is highly dependent on specific assets, it can vary widely. There are legitimate, well-run companies whose stocks are traded over-the-counter. Don’t forget to DYOR before investing in OTC stocks.
disclaimer: Please note that the content of this article does not constitute financial or investment advice. The information contained in this article is the opinion of the author only and should not be construed as offering trading or investment recommendations. We make no warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional random movements. Any investor, trader or regular crypto user should research multiple points of view and be familiar with all local regulations before making an investment.

