IOTA Tech stimulates the circular economy
TL;DR:
In partnership with Digimarc, we deliver distributed ledger technology (DLT) to help track and trace the recycling journey of plastics. The use case involves collecting and recycling plastic waste from agriculture, and converting it into bioplastics used in consumer products, such as plastic bags. It implements DPPs for both intermediate and final products, ensuring B2B and B2C verification respectively, and uses the GS1 EPCIS 2.0 standard for recording supply chain events, with evidence stored in the IOTA ledger to support provenance claims of products to support.
Plastic mulch film is an integral part of modern agriculture. It provides essential functions such as suppressing weeds, save waterand retention of methyl bromide, a powerful disinfectant and ozone depleter. However, the resulting plastic waste poses significant environmental problems and often ends up in landfills or the like pollutants.
One solution is to recycle it into biodegradable plastic (bioplastic) products. However, the process – which involves multiple stakeholders and advanced technology – is complicated, expensive and subject to different national regulations: in 2022, the OECD reportedthat “only 9% of plastic waste is recycled, while 22% is poorly managed.” An immutable and verifiable solution for accurately tracking the journey of plastic waste as it undergoes the recycling process is therefore highly valuable.
As part of the European Blockchain PCPFunded by the European Commission, the IOTA Foundation collaborated with an enterprise software and services provider Digimarc, And Agro2Circulaira European project focusing on upcycling agri-food waste and plastics with around 50 partners, to develop the prototype of the Digital Product Passport (DPP) solution for plastics. It aims to support the circular economy by closely monitoring and documenting the life cycle of plastic mulch films used in the agri-food industry.
Introduction of digital product passports
Digital Product Passports (DPPs) ensure transparency and traceability in the product lifecycle. The DPP for Plastics prototype solution contains data on the life cycle of plastic, from its disposal by waste producers to its transformation into new market-ready products by manufacturers, gradually including commercial intermediates (such as recycled polyethylene pellets).
Chain of events leading to the DPP for Plastics
Waste production phase
Let’s start with the Waste producer. Imagine a farm that uses plastic mulch film for crop protection. Like all participants in this step-by-step description, the farm has its own decentralized identification (DID) in the IOTA ledger.
After harvest, the farm collects the used plastic, documenting the type and date of use as a supply chain event. This data helps track the origin and composition of the waste. The farm signs the data with its unique DID to create a signed JSON document, expressed using EPCIS 2.0, and comparable to a verifiable reference (VC). The document is hashed to create a digital fingerprint of the dataset, and the hash is stored in a block on the IOTA Tangle. The block is confirmed on the Tangle and re-read along with a Proof of Inclusion (PoI), which allows the farm to prove itself to a verifier – this could be any other participant in the recycling supply chain, as all participants can also act as data verifiers – that the block was at some point part of the former Tangle, even if this part has already been pruned from network nodes to limit storage demand.
Waste management phase
Then an authorized one Waste manager collects the plastic waste. It records when and where the waste was collected and its journey to the recycling facility as a supply chain event.
Recycling phase
The waste ends up at a recognized company Recyclerwhere a treatment is applied to the plastic to produce new raw materials. The recycler records the recycling process, including the type of recycling and the output materials. This data has been made verifiable for transparency.
Production phase
These recycled materials are then delivered to a Manufacturerthat converts recycled plastic into new products, such as environmentally friendly packaging or bioplastic used as mulch film. The new products will have unique DPPs, where all information captured to date during the supply chain journey is stored via a link between Digimarc’s product identity management platform Illuminate and every supply chain event. It documents the materials used, the production process and the specifications of the final product. It also verifies the DPPs of the raw materials to ensure sustainability.
Quality assurance
Some of the processes, but also the product specifications, can be certified by a third party Quality assurance. This is also signed by the corresponding DID and linked to the product’s DPP information.
Consumer interaction
Consumerswhich in this case study are largely B2B entities, purchase these manufactured bioplastics – for example, a farmer purchases the bioplastic mulch film. Consumers scan the QR code on the packaging to access the DPP, which allows them to verify the origin and sustainability of the product. This transparency creates trust among their own customers.
Control
Finally one accountant steps in to verify the accuracy of the data. They ensure compliance with environmental regulations, protect against fraud and identify potential operational improvements.
Ensuring trust and transparency
During this entire process the EBSI trust framework models and verifies the identities and relationships of all actors. Usage GS1 EPCIS 2.0 standards and supply chain events such as shipping, receiving, packaging, transformation and classification are captured and recorded. Each product gets one GS1 digital link via Illuminate, linking all traceability events to build the DPP view.
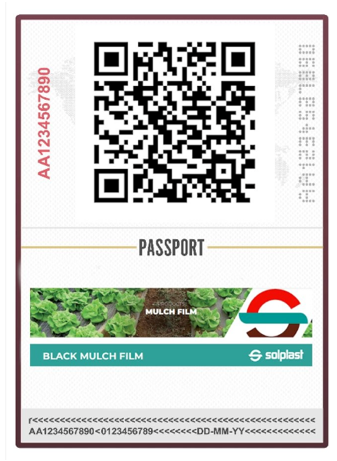
Digital connection with the DPP via a QR data carrier
Digital link to the DPP via a QR
The physical products are identified by a GS1 Digital Link using a carrier of their choice, in this case a QR code, which is linked to their digital passports, allowing easy access and verification via a DPP web interface. This interface displays the status and information of the DPP at any time and updates it accordingly, for example if a DPP needs to be invalidated, an additional business event marks it as outdated, and this update is reflected in the DPP web interface.
DPP details as seen in the DPP web interface
In this system, every party, from the waste producer to the auditor, plays a crucial role in ensuring the transparency, traceability and sustainability of agricultural plastics, supporting a robust circular economy.
Conclusion
Using blockchain technology, our prototype DPP solution for plastics brings transparency, traceability and integrity to the life cycle of agricultural plastics, promoting a circular economy and reducing environmental impact. This not only promotes sustainability, but also provides valuable insights for both companies and consumers. You can read Digimarc’s report on the DPP here.
Download our DPP prototype presentation
Our Technology Adoption Team is leading the commercialization of the DPP electronics prototype solution in collaboration with a network of partners – our first market-ready solution is the recently announced Eviden Digital Passport solution powered by IOTA – to track the life cycle of physical and virtual products: from (car) batteries (for electric vehicles and more), plastics, rubber, tires and chemicals to electronic or virtual assets such as intellectual property rights. For more information about these options, please contact [email protected].
Links in this article
Epic gardening website: 18 pros and cons of using plastic mulch in the garden
BBC website: Why the food plastic problem is bigger than we realize
OECD press release: Plastic pollution is growing relentlessly while waste management and recycling fall short, says the OECD
Website: Digimarc.com
Website: Agro2Circulair.eu
European Commission webpage: European blockchain pre-commercial purchasing
Blog post from the IOTA Foundation: Introducing the Eviden Digital Passport solution, powered by IOTA
Blog post from the IOTA Foundation: Ratification of the EPCIS 2.0 standard
European Commission/EBSI webpage: Trust model of the issuer
Digimarc blog post: EPCIS 2.0: Transforming the Global Supply Chain
Video: GS1 Digital Link Layer Cake
Digimarc webpage: Digimarc Illuminate Platform
Digimarc blog post: Testing a digital product passport for plastic recycling