The price from Bitcoin rose to $ 95k, but the 24-hour graph reveals increased volatility, with Oi reach those record levels Above $ 32 billion.
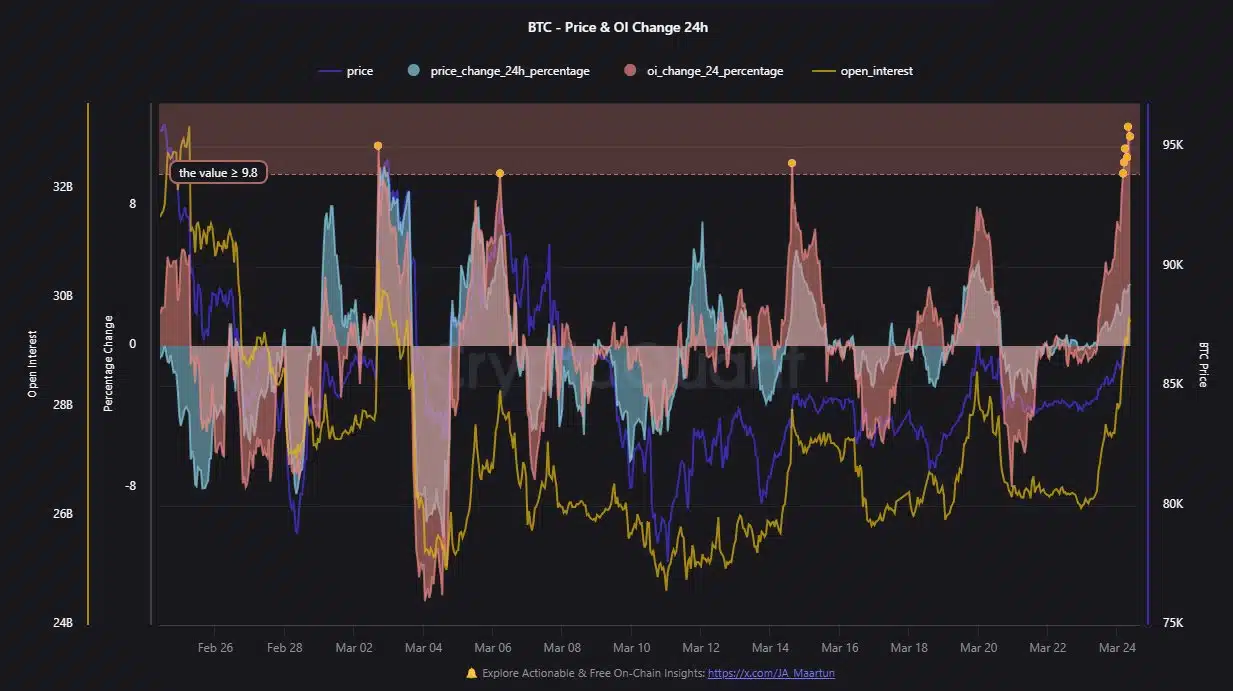

Source: Cryptuquant
In the last 24 hours, Bitcoin saw a considerable price increase, accompanied by remarkable inflow of lifting tree positions. In addition to the price, OI has hit up, which suggests that traders bet on further profit.
However, OI peaks of more than 9.8% have traditionally been a precursor of sharp corrections. If the price momentum falter, surviving positions can relax, creating rapid sale.
Bitcoin Leverage: Breakout or Breakdown?
While OI $ 32 billion crosses, the growing leverage feeds the Bitcoin meeting. However, this inflow of capital creates a fragile arrangement where even small withdrawals could activate liquidations.
A rapid price increase in combination with excessive leverage increases the risk of stairy liquidations, making it potential for reinforced price fluctuations.
If Bullish Momentum persists, Bitcoin can enter a parabolic phase and push prices that go beyond the current highlights. On the other hand, if the price suddenly drops, this can cause a wave of liquidations, which leads to a sharp correction.
Monitoring of shifts in OI and financing percentages are crucial for assessing market sentiment and identifying potential trends.
FOMO may be riding Bitcoin higher, but at what costs?
Bitcoin’s climb to $ 87.5K has inflamed a wave of Fomo, in which traders come in to take advantage of the momentum. The OI has further increased this increased speculation, which indicates the growing leverage on the market.
Although this emotional buying spree Bitcoin can push into unknown territory, it also increases the risk of a sharp correction if sentiment shifts.
History warns that such leverage rally rallies are often followed by fast reversations.
If the sentiment shifts or leverage, the same traders who increase prices can quickly be on the wrong side of a quick correction.
As the rally continues, it is crucial to anticipate the financing percentages and OI shifts to anticipate potential reversations.

