What is a Depin?
Decentralized physical infrastructure networks (Depins) connect the physical and digital worlds with the help of blockchain technology. They reward participants with tokens for offering services that are publicly recorded on the blockchain.
Imagine a Depin as a cooperation system, similar to a public library. In this scenario, blockchain Acts as a detailed catalog, which keeps track of the location of each book and the credit history. It is open to everyone to use. Just as libraries depend on the participation of readers, Depin projects thrive on the collective contributions of their users.
Depins make networks of physical sources possible – such as WiFi or data storage – so that individuals can share these sources directly with others without needing an intermediary.
How does Depin work?
Although WiFi signals and data may seem digital, they depend on physical components such as routers, servers and antennas. These devices form the basis of the network, making them part of the physical infrastructure.
Depins work on block chains and use tokens or cryptocurrencies for transactions. This ensures transparency and traceability. Users who contribute sources, such as hosting a wireless hotspot or providing storage, are rewarded with tokens.
The blockchain serves as a virtual manager, who takes every action, such as service fairs and network updates. With this open system, everyone can participate in offering services, such as internet access or energy management, without needing special approval.
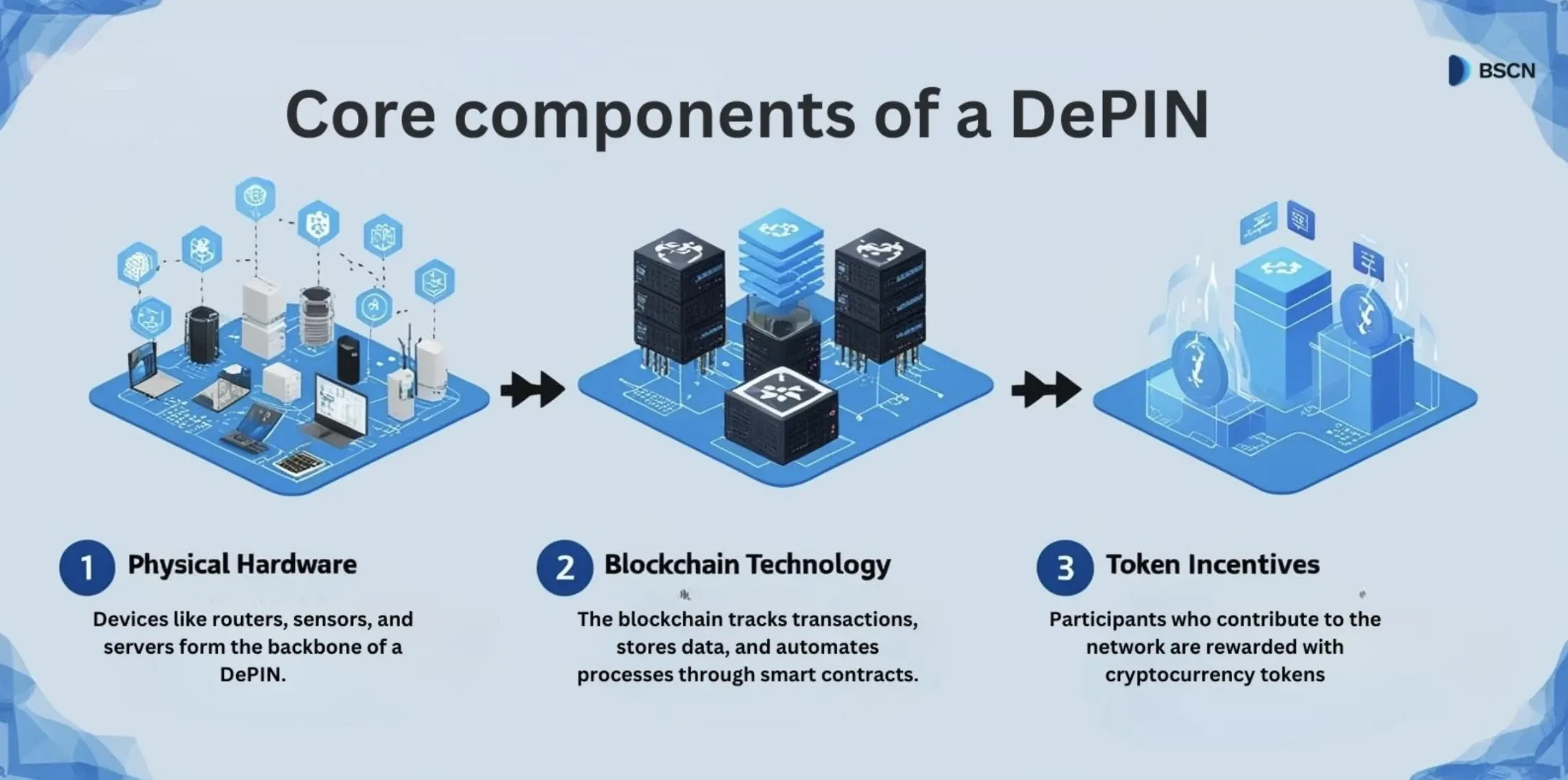
The three most important components of a Depin
Why are Depins important?
Depins make infrastructure such as energy systems, communication networks and transport more accessible, more efficient and adaptable. In contrast to traditional systems that are controlled by large companies, Depins distribute control among daily participants. This allows smaller groups or individuals to manage resources such as electricity, internet or storage.
They also improve reliability by staying operational, even during crises. Their decentralized nature promotes competition, lowers costs and encourages innovation. In addition, Depins eliminate the need for considerable investments in advance, making a faster implementation and adjustment for local needs possible. This approach is leveling the playing field for small companies and entrepreneurs and creates new opportunities to offer services.
Components of a Depin
Depin’s rely on three primary components:
- Physical hardware: Devices such as routers, sensors and servers form the backbone of a Depin. These physical nodes connect the digital blockchain with the real world.
- Blockchain technology: The blockchain records all activities and provides transparency. It follows transactions, saves data and automates processes through smart contracts.
- Token stimuli: Participants who share sources or contribute to the network are rewarded with cryptocurrency -tokens, so that they motivate to maintain and expand the system.
For example, Smart contracts And Internet of Things (IoT) Devices automate tasks such as energy distribution or data collection. These systems ensure efficiency and eliminate the need for intermediaries.
Traditional infrastructure versus Depins
Traditional infrastructure is usually centralized, controlled by a single entity or company. This approach can lead to inefficiencies, high costs and limited access. Depins, on the other hand, distribute ownership and management, which makes direct cooperation between users and providers possible.
Examples of Depin Use Cases
Storage solutions
Create Depins decentralized storage Networking by distributing data on multiple devices. This makes data storage safer and more reliable compared to centralized systems. Projects such as Filecoin break data in smaller pieces, distribute them over the network and use coding to keep it safe and accessible.
Wireless connectivity
Depins offer peer-to-peer wireless networks where devices communicate directly. Projects such as Helium Have individuals set up hotspots to offer IoT connectivity. In exchange, they earn cryptocurrency. This model reduces the need for centralized hubs and promotes innovation in areas such as agriculture and logistics.
Distribution of energy
Depins can feed local microgrids with renewable energy, such as solar panels. Excess energy can be stored in nearby batteries and distributed during periods with a lot of application. These systems support green energy initiatives and improve overall reliability. Smart schedules help in real time to balance the energy device and offer in energy.
Decentralized sensors
Depins also use distributed sensors to control things such as traffic, environmental conditions or infrastructure health. Each sensor collects and shares data safely in the network. Participants who provide information can earn cryptocurrency solutions. This decentralized data collection goes to city planning, agriculture and environmental monitoring.
Steps to build a Depin
Making a Depin requires careful planning and implementation. Here is a step -by -step sketch:
- Define objectives: Clearly outlines the goals of your Depin, such as improving energy efficiency or expanding internet access. Identify the specific type of infrastructure on which you want to concentrate.
- Choose a blockchain platform: Select a blockchain that meets your needs in terms of scalability, speed, security and costs. Consider platforms with robust functions and strong management models.
- Set up a token economy: Design a tokens system to handle transactions and rewards. Create a board mechanism, such as token -based votes, to include stakeholders in decision -making.
- Develop smart contracts: Build safe and transparent smart contracts to automate transactions and manage sources efficiently. Test them thoroughly to guarantee reliability.
- Implement hardware: Set the physical infrastructure, such as sensors, routers or smart meters. Make sure these devices seamlessly integrate with the blockchain.
- Attract participants: Collect a mix of resource providers and users. Use token rewards or models for sharing income to encourage participation in and grow the network.
- Implement security measures: Protect your Depin with coding and security protocols to protect data and prevent unauthorized access.
Challenges and disadvantages
Although Depins offer many benefits, they also come up with challenges:
- Regulatory obstacles: Many countries lack clear legal frameworks for projects on blockchain and crypto-based projects. Staying compliant with existing laws is essential.
- Security risks: Decentralized systems must balance transparency with privacy. Smart contracts and sensitive data can be vulnerable to cyber threats if they are not properly secured.
- Complexity: Managing physical devices and integrating them with blockchain technology can be technically demanding, which requires significant expertise and resources.
Depins reform how infrastructure works by decentralizing control and encouraging cooperation. They open the door to innovative solutions for storage, connectivity, energy and then. Although challenges exist, it makes potential for accessible and efficient systems Depins a promising option for the future of physical and digital integration.